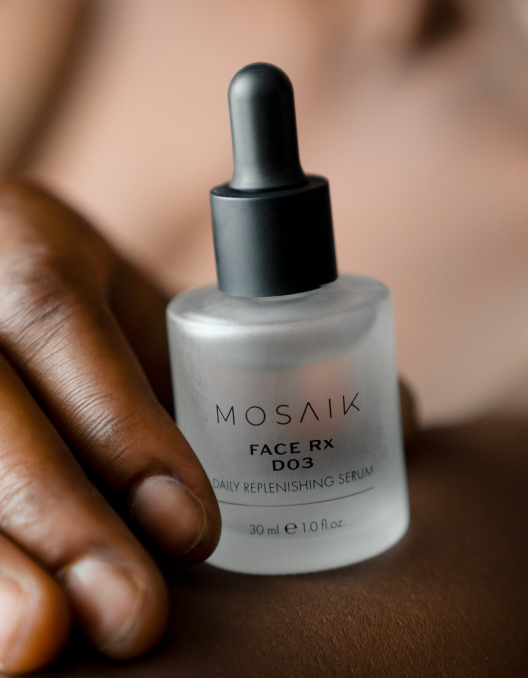
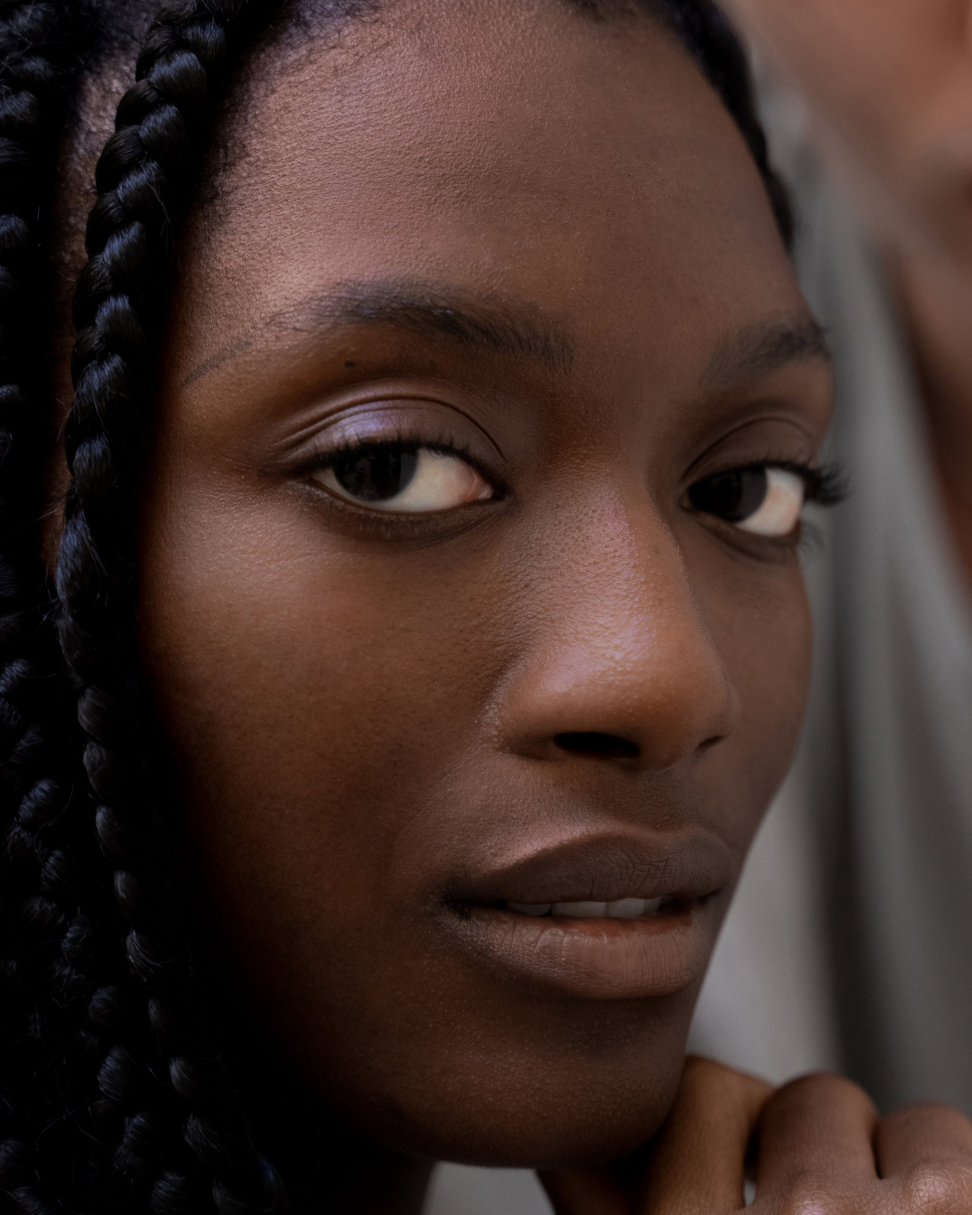Need any support or advice on our MOSAIK products?


Expert Advice & Skin Science
Experience expert skincare knowledge and advanced science, uniquely infused with the wisdom of Japanese skincare rituals and smart ingredient formulation.
In this section, you'll find trusted guidance from leading experts, practical tips rooted in Japanese ritual, and educational resources to help you understand your unique skin.
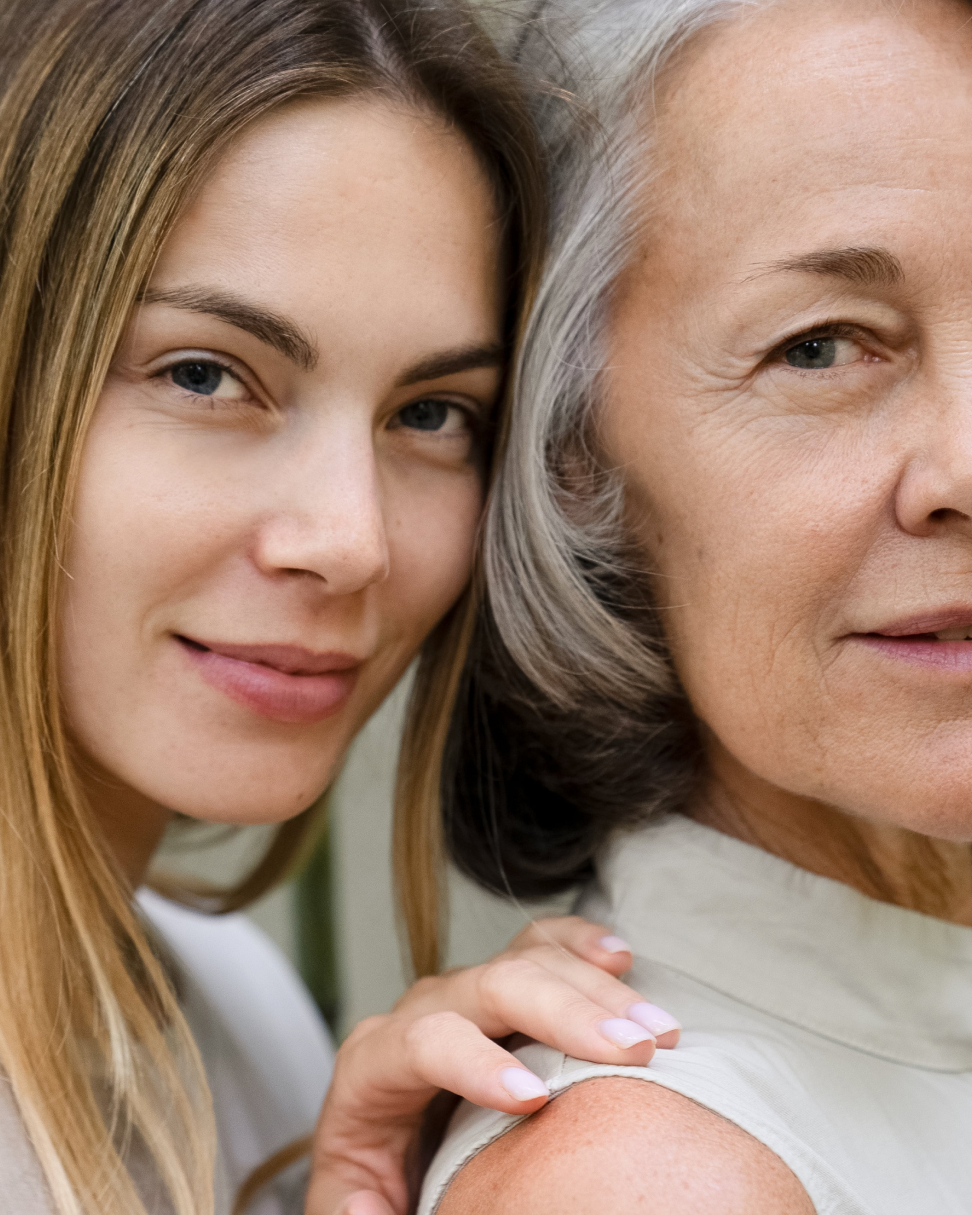
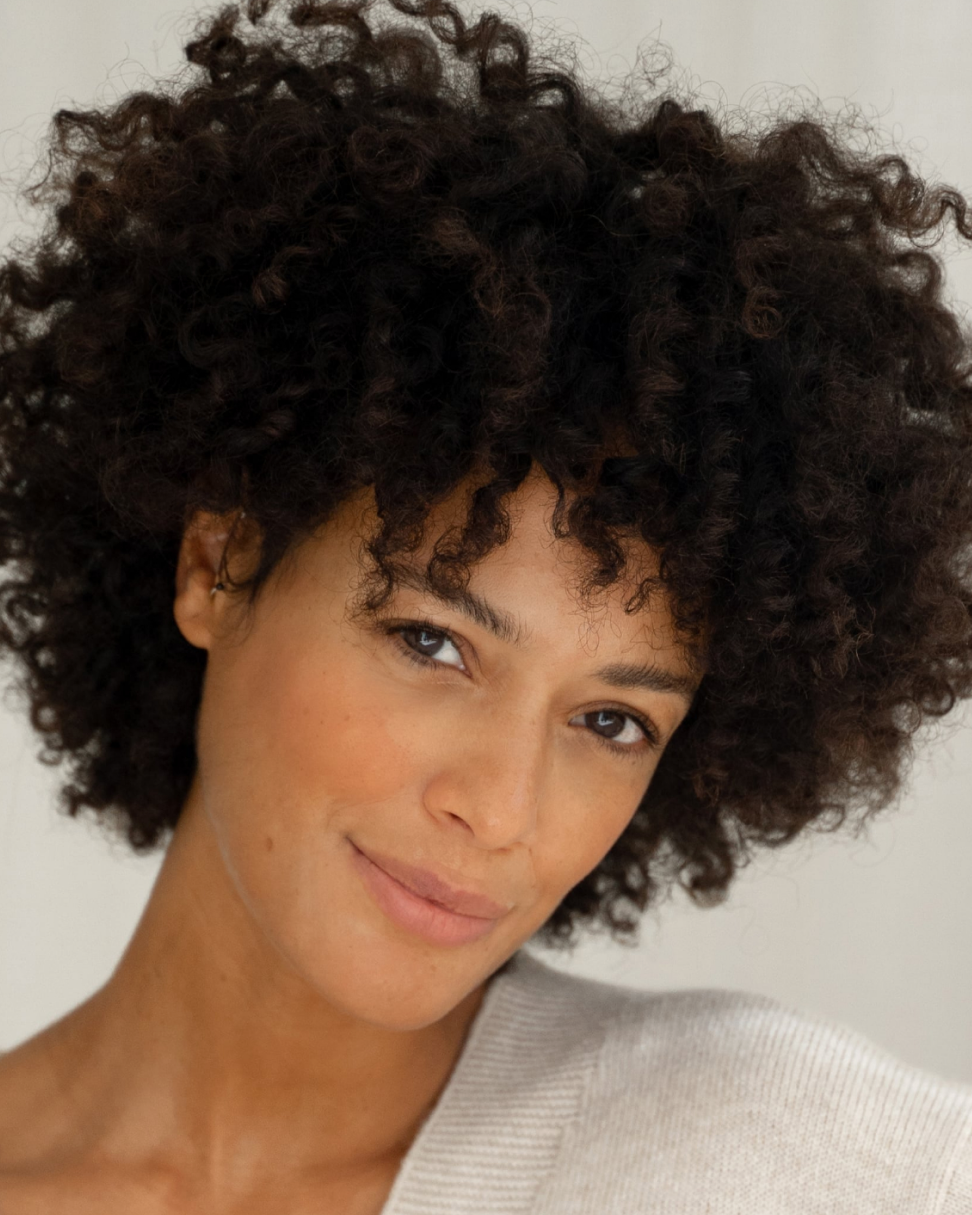
Understanding your genetic ethnic origin (ancestry) may not only help you understand your skin and address specific skin concerns, but also give you insight into effective, preventative care measures. While visible pigmentation (melanin levels) is more frequently reflective of skin condition and susceptibility to certain skin concerns, it is not the only causation factor. It is also essential to understand the contribution that your overall state of wellness has, in both a holistic and all embracing way.

Differences of Skin Conditions
Click below on a skin condition to learn more:
Click below on a skin condition to learn more:
Understanding Your Skin
Skin Type I (Very Pale or Ivory)
Skin Type II (Pale or Fair)
Skin Type III (Fair or Beige)
Skintype IV (Beige or Olive)
Skin Type V (Medium to Dark)
Skin Type VI (Dark to Very Dark)
PROTECTION
1. Harmful Agents.
2. Excessive loss of moisture and protein.
3. Mechanical, thermal and other physical injury.
4. Harmful effects of UV radiation.
THERMOREGULATION
One of the skin's important functions is to protect the body from cold or heat, and maintain a constant core temperature. The secretion and evaporation of sweat from the surface of the skin also helps to cool the body.
SENSATION
Skin is the 'sense-of-touch' organ that triggers a response if we touch or feel something, including things that may cause pain as well as pleasure.
IMMUNE DEFENSE
The skin is an important immunological organ, made up of complex key structures and cells. Depending on the immunological response, a variety of cells and chemical messengers (cytokines) can be activated and function to protect the body.
BIOCHEMICAL FUNCTIONS
The skin is involved in several biochemical processes. For example, in the presence of sunlight, vitamin D is synthesized, which is essential for the normal absorption of calcium and phosphorus (required for healthy bones).


Skin of Colour:
A Historical Perspective

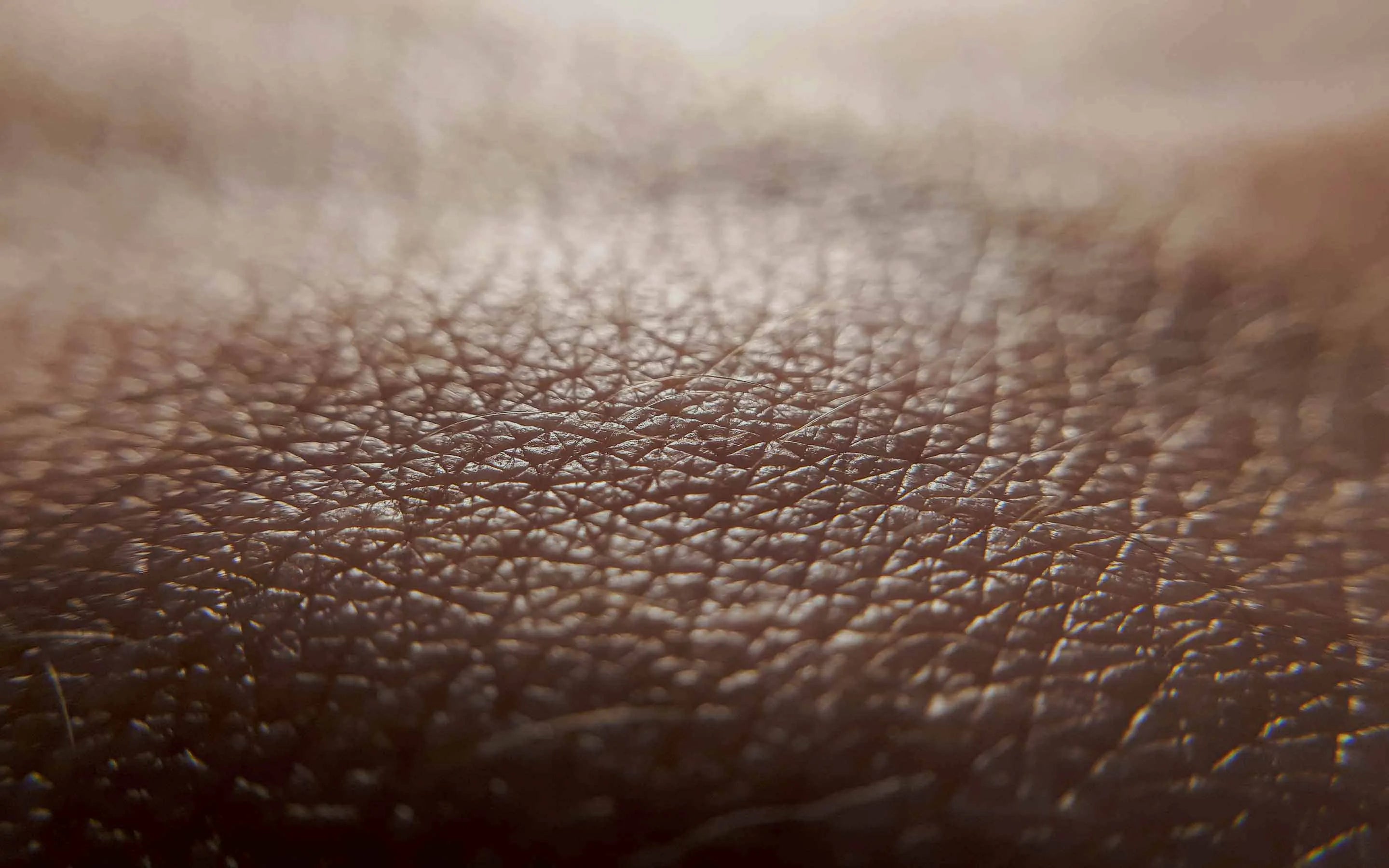
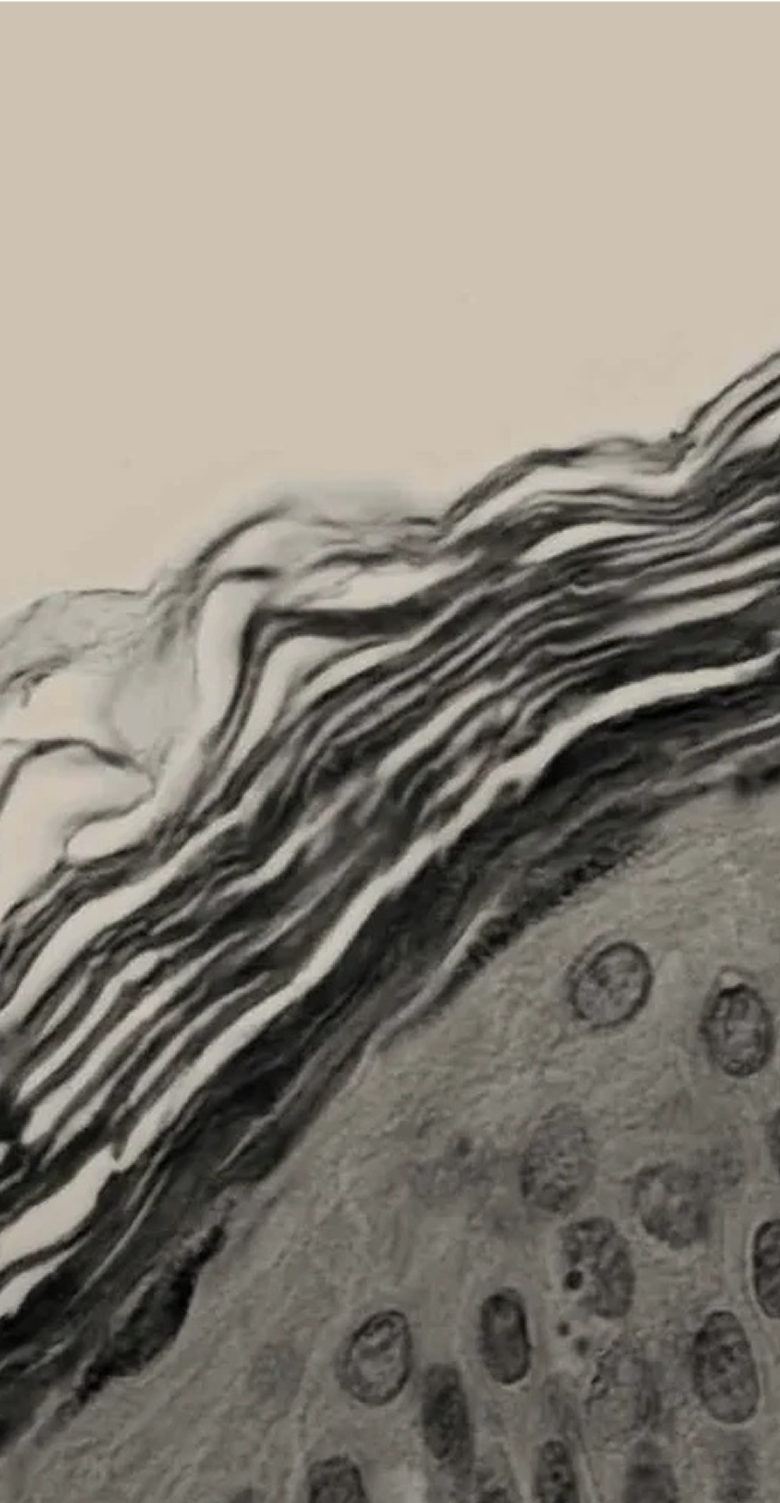
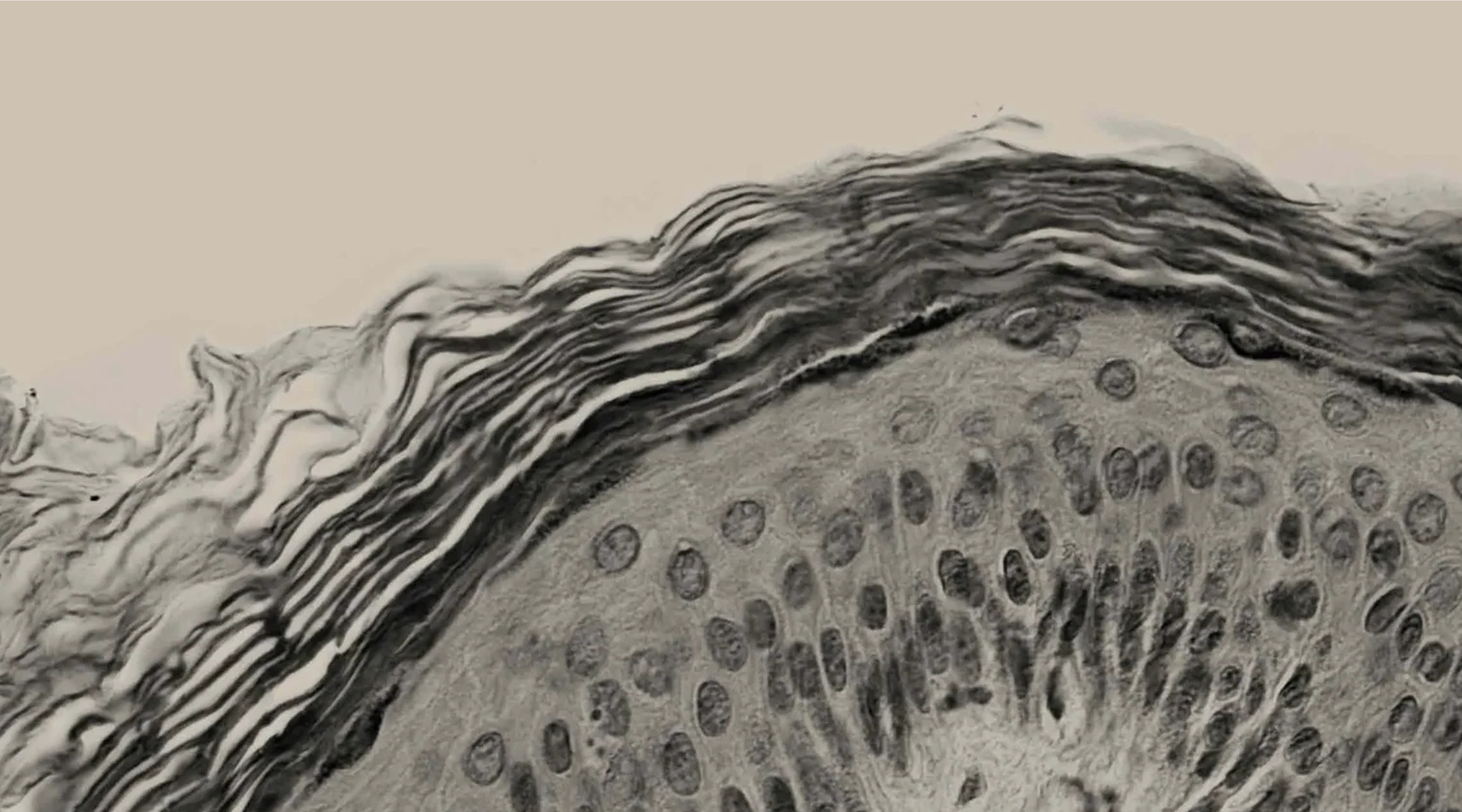
THE SCIENCE OF THE MELANIN PIGMENTARY SYSTEM
Although there has been much philosophical, religious, mythological and even scientific speculation on the causes of skin colour, science and medicine has provided us with the biological answers to these clinical observations.
The skin has epidermal units that are responsible for melanin production and distribution, a process called melanogenesis. These units are composed of a melanocyte surrounded by keratinocytes and regulated by a closed paracrine system. Melanin is the primary determinant of skin, hair, and eye colour. And plays a critical role in photo protection due to its ability to absorb ultraviolet radiation (UVR).
Featured Articles
Understanding your skin empowers you to make more informed skincare decisions. Our Journal covers everything from Japanese skincare secrets to treatment insights and ingredient guides.
read all